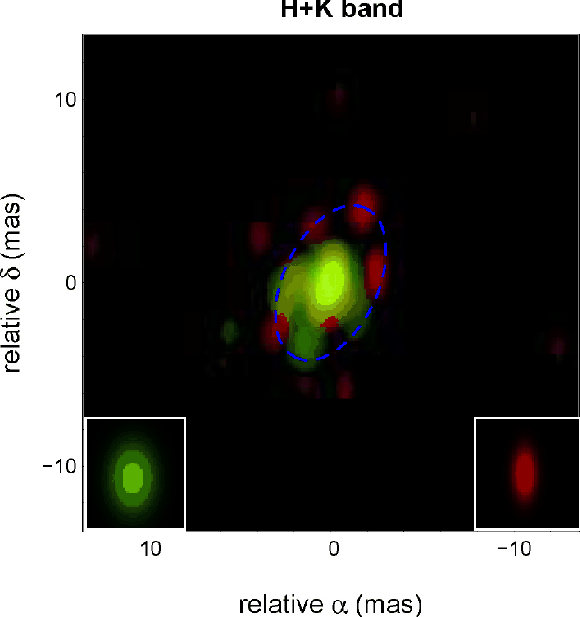
The very close environments of young stars show complex morphological structure as a result of planet formation, star-disk interactions, mass accretion, and ejection.The two-color reconstructed image (H band in green, K band in red) of the young star MWC 275 (HD 163296) is based on data collected with various interferometers (VLTI, IOTA, KeckI and CHARA). The blue ellipse traces the location of the main secondary blobs of the K-band emission. The sub-panels indicate the Gaussian beam at the resolution in each wavelength band. The images detect several significant features related to an inclined asymmetric flared disk around MWC 275 with the strongest intensity at about 4-5 mas. These images confirm that the morphology of the close environment of young stars is more complex than the simple models used in the literature so far.
References:
Milli-Arcsecond Images of the herbig Ae Star HD 163296
Renard, S., et al., 2010, Astronomy and Astrophysics, 519, 26
A Tale of Two Herbig Ae Stars - MWC 275 and AB Aurigae: Comprehensive Models for SED and Interferometry
Tannirkulam, A., et al., 2008, Astrophysical Journal, 689, 513
Strong Near-Infrared Emission Interior to the Dust Sublimation Radius of Young Stellar Objects MWC 275 and AB Aurigae
Tannirkulam, A., et al., 2008, Astrophysical Journal, 677, L51-54